Plastics are synthetic or semi-synthetic polymers that are derived from oil or petroleum. They are produced by chemical reactions that join the monomers together into long chains, called polymerization or polycondensation. Plastics can be classified into two main categories: thermoplastics and thermosets. Thermoplastics can be melted and reshaped multiple times, while thermosets cannot be reprocessed once they are cured or hardened.
Some examples of common plastic polymers are:
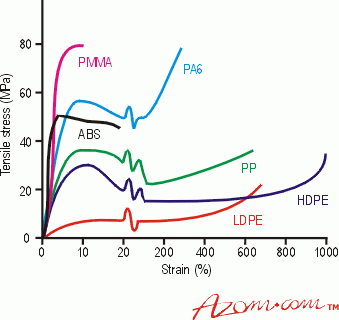
• Polyethylene (PE): A thermoplastic polymer that is used for packaging, bottles, bags, pipes, and films. It has a simple structure of repeating ethylene units and can be classified into different grades based on its density and molecular weight.
• Polypropylene (PP): A thermoplastic polymer that is used for containers, automotive parts, fibres, and medical devices. It has a similar structure to polyethene but with a methyl group attached to every other carbon atom. It has higher strength, stiffness, and heat resistance than polyethene.
• Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): A thermoplastic polymer that is used for pipes, fittings, siding, flooring, and cables. It has a structure of repeating vinyl chloride units and can be made flexible or rigid by adding plasticizers or stabilizers. It has good resistance to chemicals, fire, and weathering.